Current Situation and Technology Trends of E-waste Recycling
With the rapid development of my country's economy and the rapid progress of science and technology, people's living standards have been continuously improved, the number of electrical and electronic equipment and motor vehicles has continued to increase, and the replacement cycle has shortened. The growing trend year by year provides sufficient raw materials for the electronic waste, scrapped motor vehicle dismantling industry and waste electronic equipment recycling industry.
Electronic waste contains a large number of valuable resources that can be recycled and reused, mainly including: ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals, plastics, glass and others. Among them, steel is the largest part of electronic waste, accounting for almost half of the total weight; followed by plastics, accounting for about 20%-25% of the total weight; non-ferrous metals (including precious metals), accounting for about 13% of the total weight (of which , copper accounts for 7%). In addition, it also contains ceramics, rubber, etc., which also have recycling value.
E-waste is a valuable resource. Strengthening the research and application of e-waste metal recovery technology is of great significance both from an economic perspective and from an environmental perspective. Due to the complexity and variety of e-waste, it is difficult to recover metals using any technology alone. The development trend of electronic waste treatment technology in the future should be the industrialization of treatment forms, the maximization of resource recovery and the scientificization of treatment technology. Studying the recycling of waste PCB can not only protect the environment and prevent pollution, but also facilitate the recycling of resources, save a lot of energy, and promote the sustainable development of the economy and society.
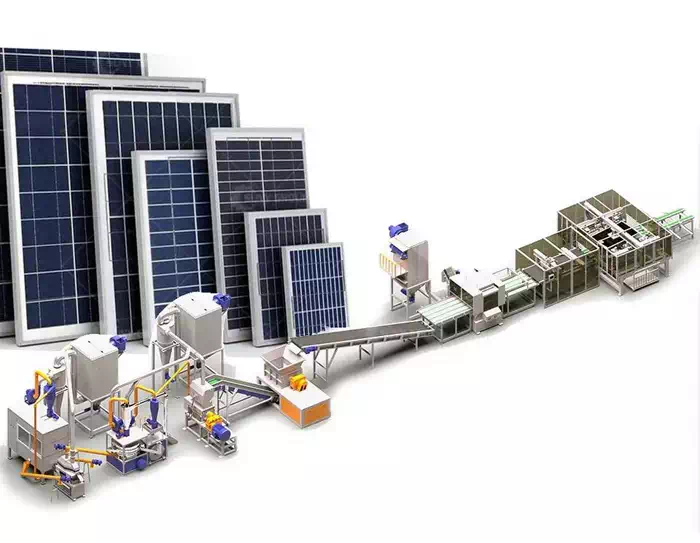
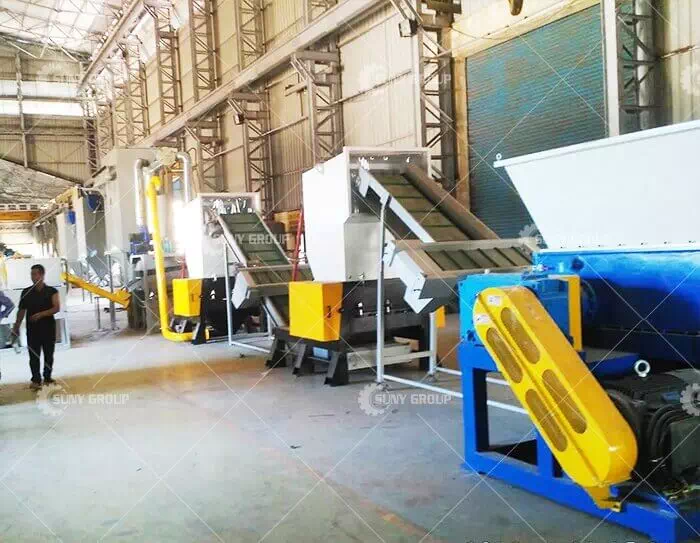
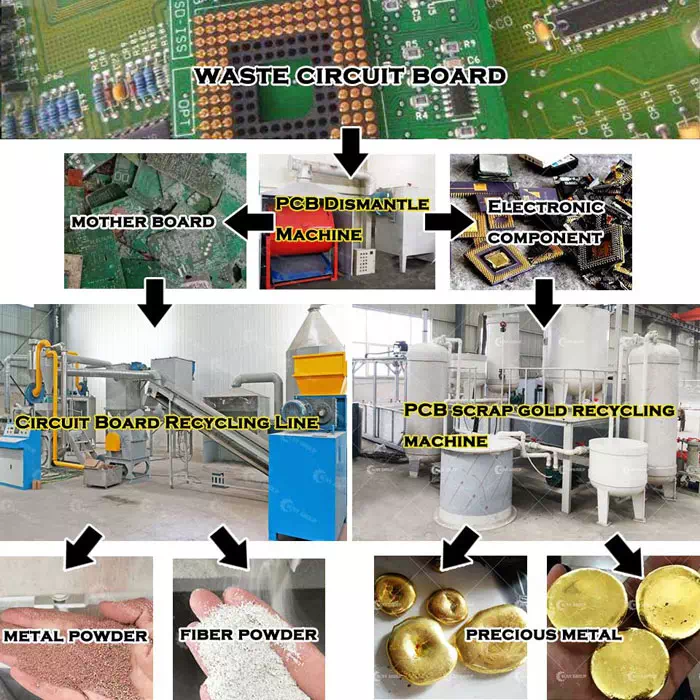
Electronic waste waste circuit board recycling technology process
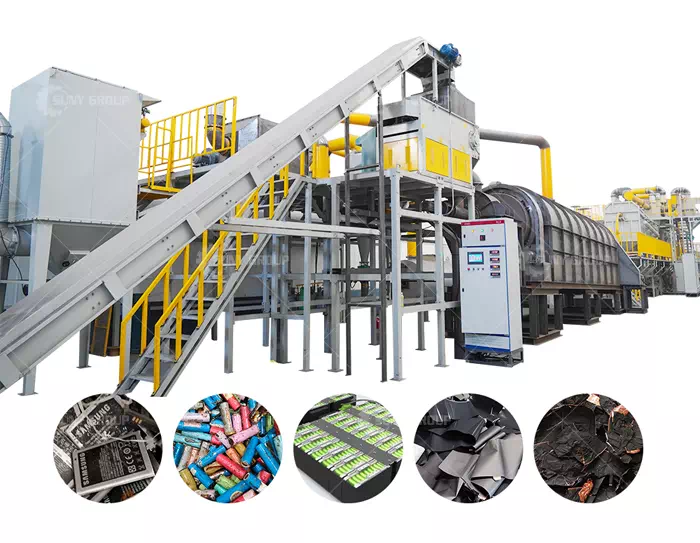
The environmentally friendly circuit board recycling equipment process adopts dry physical crushing and sorting. Complete dry separation system; its technology is advanced, and no new problems are generated in the production process, such as pollution to the environment. There is no waste gas and sewage, and no noise pollution. The main core equipment adopts noise shielding room. The production noise in the workshop meets the safety production standards, and the dust passes through the filtration system to meet the environmental protection standards, safety protection and other process designs.
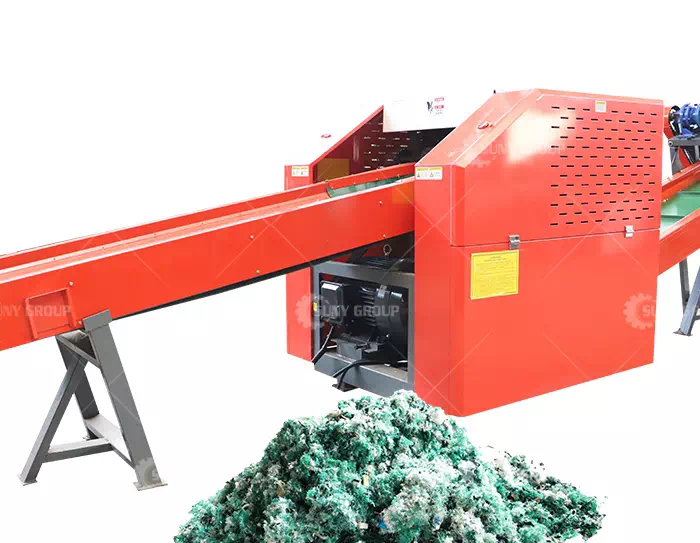
Circuit board recycling equipment The primary crusher uses two-roller or three-roller electrostatic and shearing crushing methods to cut large pieces of waste circuit boards. The crushing process adopts the method of rotary shearing and hammering mixed crushing for secondary crushing of materials of a certain size. To ensure whether the crushed particle size meets the process requirements, it is equipped with a variety of vibrating feeders suitable for uniform feeding of thin layers of different materials.
Preprocessing
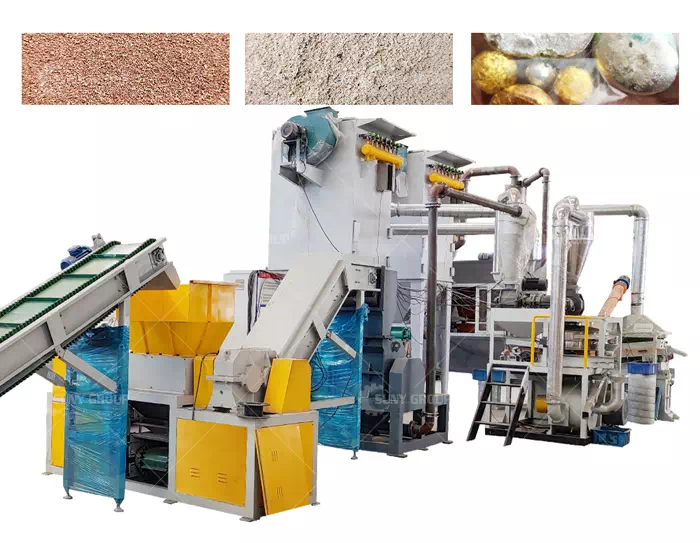
Pretreatment mainly refers to mechanical treatment, which is a means of sorting according to the differences in physical properties between materials, including density, conductivity, magnetism, surface characteristics, etc., including dismantling, crushing, sorting and other processing processes. Mechanical treatment can fully enrich valuable substances in electronic waste, reducing the difficulty of subsequent treatment. Compared with subsequent treatment, it has less pollution and lower cost, but cannot obtain precious metals with higher purity.
1. Dismantle valuable components or auxiliary equipment, and re-dismantle after passing the inspection: the purpose is usually 2 points, ○
2. Remove the components or auxiliary equipment containing harmful substances and dispose of them separately. Use: ○
Fragmentation: Using external force to destroy the cohesion and intermolecular force inside the object is the key step to dissociate the material to be recycled from the electronic waste.
Sorting: Sorting refers to the process of separating different components in electronic waste crushed products according to different physical or physicochemical properties (such as particle shape, density, etc.). It is usually divided into dry sorting and wet sorting. Pick 2 types.
Post-processing
Electronic waste can only be obtained after subsequent treatment to obtain precious metals with higher purity, but it is easy to cause secondary pollution. Subsequent processing includes pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy and biological methods, etc.
Pyrometallurgy: The basic principle of pyrometallurgy is to use a metallurgical furnace to heat and strip non-metallic substances at high temperature, so that precious metals are melted into other metal smelting materials or molten salts. separate again. Non-metallic substances are mainly printed circuit board materials, etc. Generally, scum is separated and removed, while precious metals and other metals flow out in an alloy state, and then refined or electrolytically treated. Pyrometallurgy mainly includes incineration melting process, high temperature oxidation melting process, scum technology, electric arc furnace sintering process, etc.
The method has the characteristics of simple process and high recovery rate. It can process all forms of electronic waste. The main precious metals recovered are Au, Ag, Pd and so on. However, it is easy to produce secondary pollution, such as a large amount of harmful gases emitted by incineration, and solid waste generated by scum. It was more common in the 1980s.
Hydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy: Its basic principle is to use the characteristics of crushed precious metal particles that can be leached under acidic or alkaline conditions, and separate them from electronic waste through solvent extraction, precipitation, replacement, ion exchange, electrolysis and other processes in the leaching solution. and recovered from the liquid phase.
This method can obtain high-grade and high-recovery precious metals such as Au and Ag. The recovery effect of non-ferrous metals such as Cu and Zn is also very good, and the processing cost is low. But there are the following problems: 1. It cannot directly deal with complex electronic waste; 2. The leaching agent of precious metals can only act on the exposed metal surface. When the metal is covered or wrapped in ceramics, the recovery efficiency is low; 3. The leaching solution and residue are corrosive Sex and toxicity. It is easy to cause more serious secondary pollution.
Recommend products
CONTACT US:
If you have any requirement or suggestion, please fill in the form and send to us, thanks!E-mail:sunymachine@gmail.com | Whatsapp:+8613674945231









